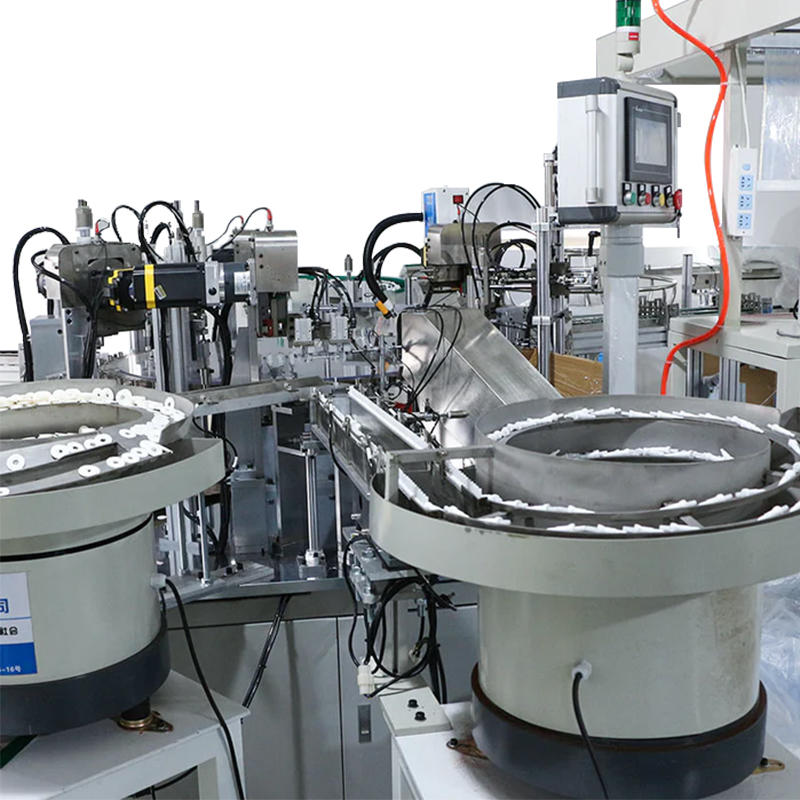
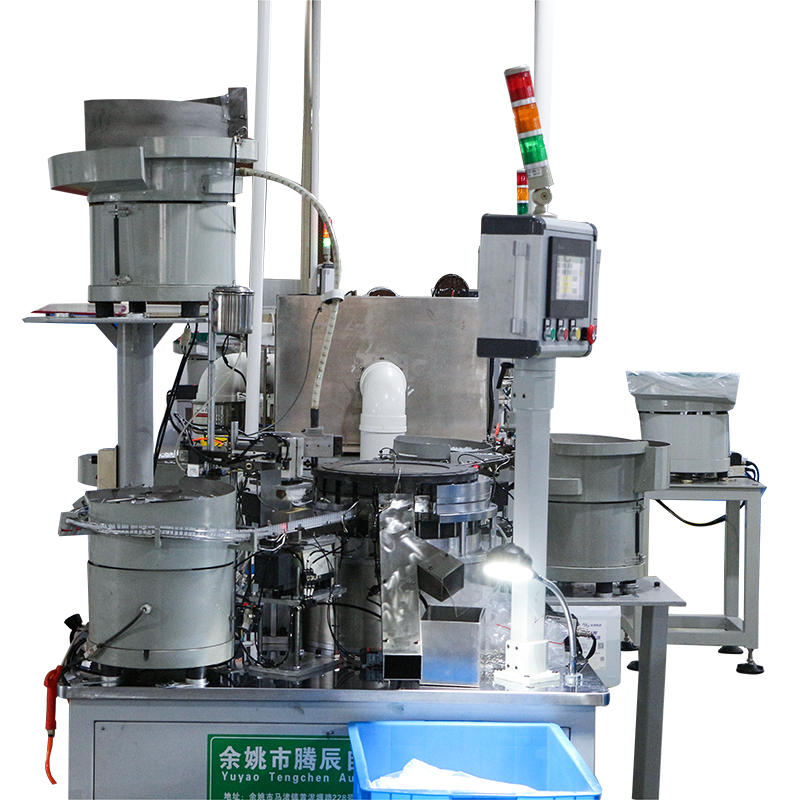
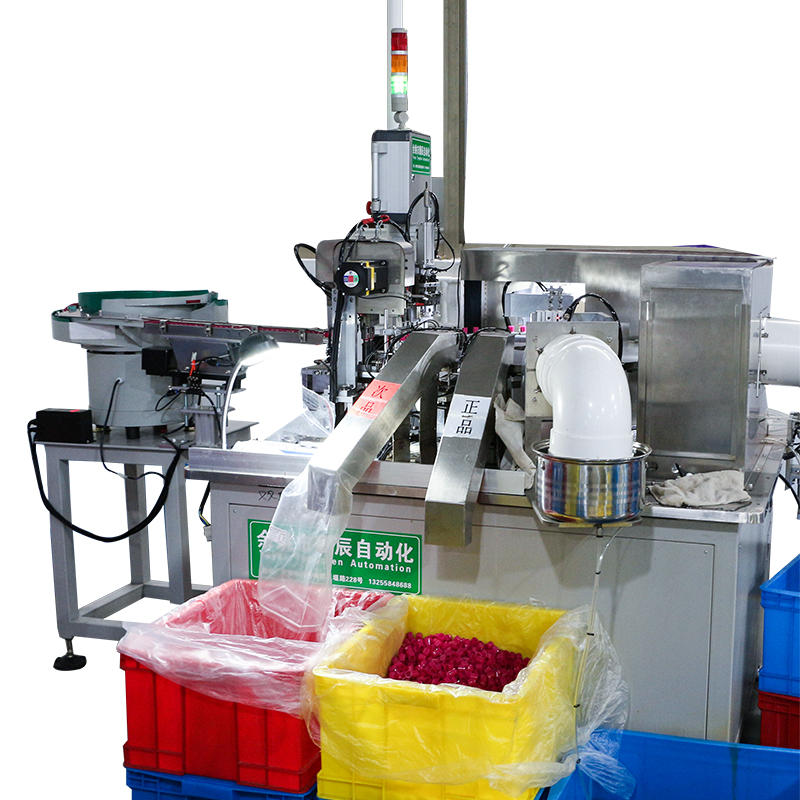
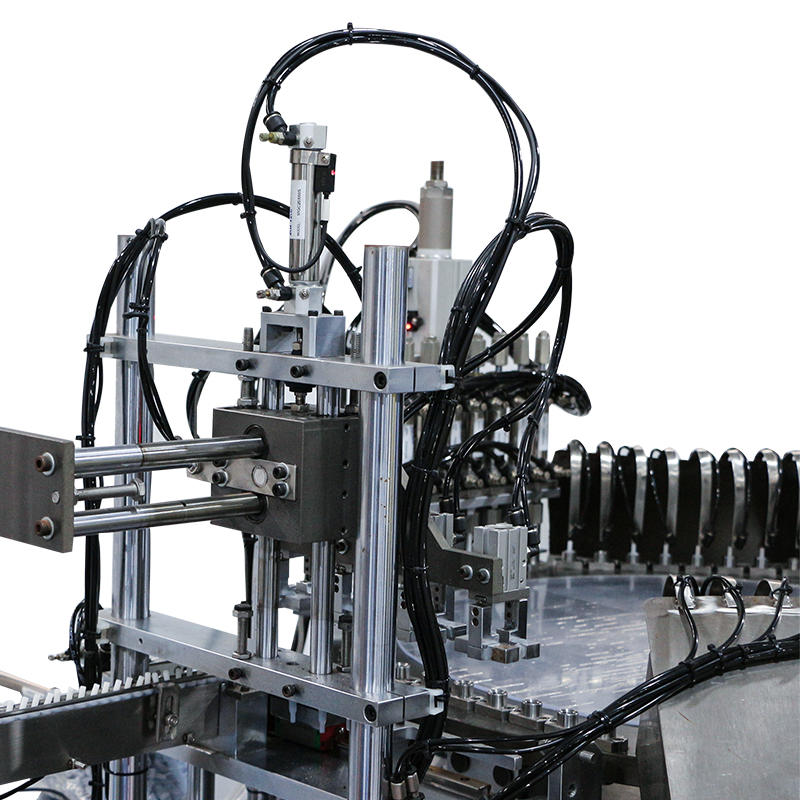
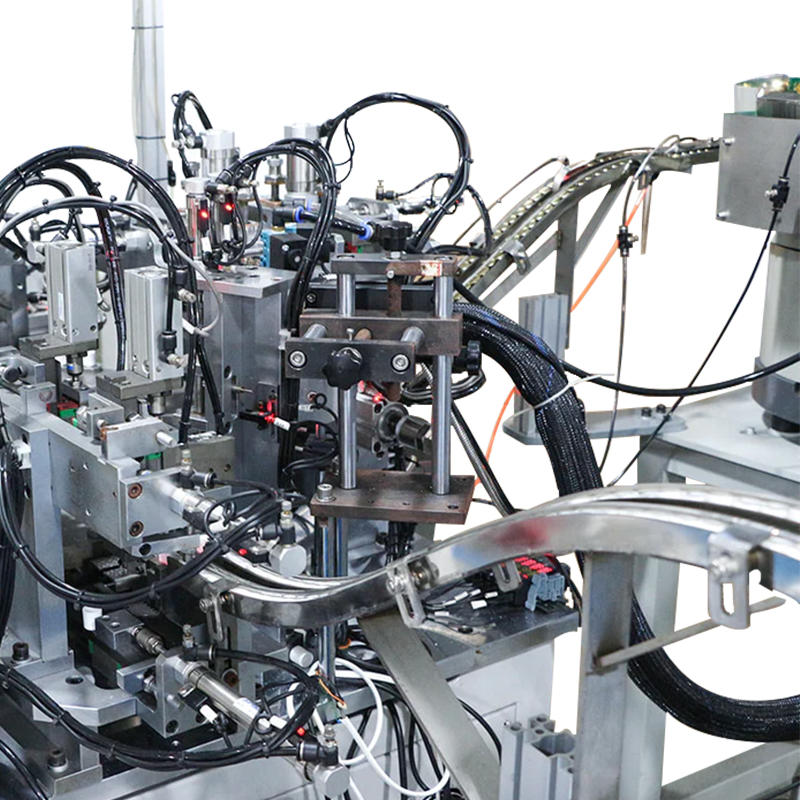
Multi-Stage Indexing System for Synchronized Component Feeding: The dropper assembly machine operates with a high-precision indexing system that divides the assembly process into a sequence of controlled stages. Whether employing a rotary indexing table or a linear conveyor, each station is designed to perform a single, repeatable task with millisecond-level timing coordination. This segmentation reduces cumulative alignment errors and provides a structured path for each component—ensuring that the rubber bulb, glass tube, and cap interact only when perfectly aligned. Mechanical cams or servo motors drive the indexer, guaranteeing consistent positioning across thousands of cycles per hour, making this structure ideal for maintaining alignment integrity during high-speed assembly operations.
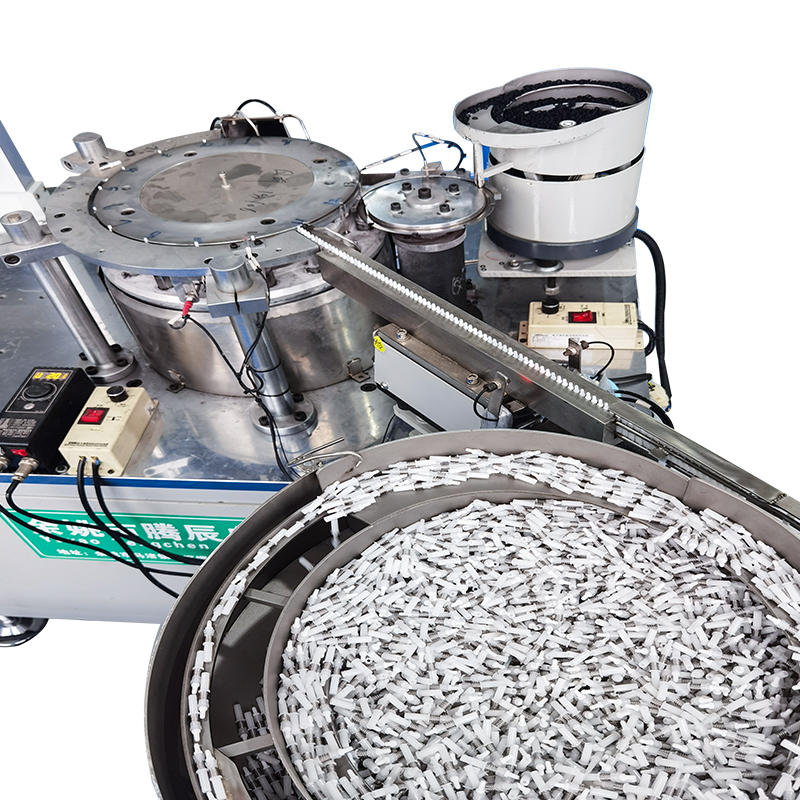
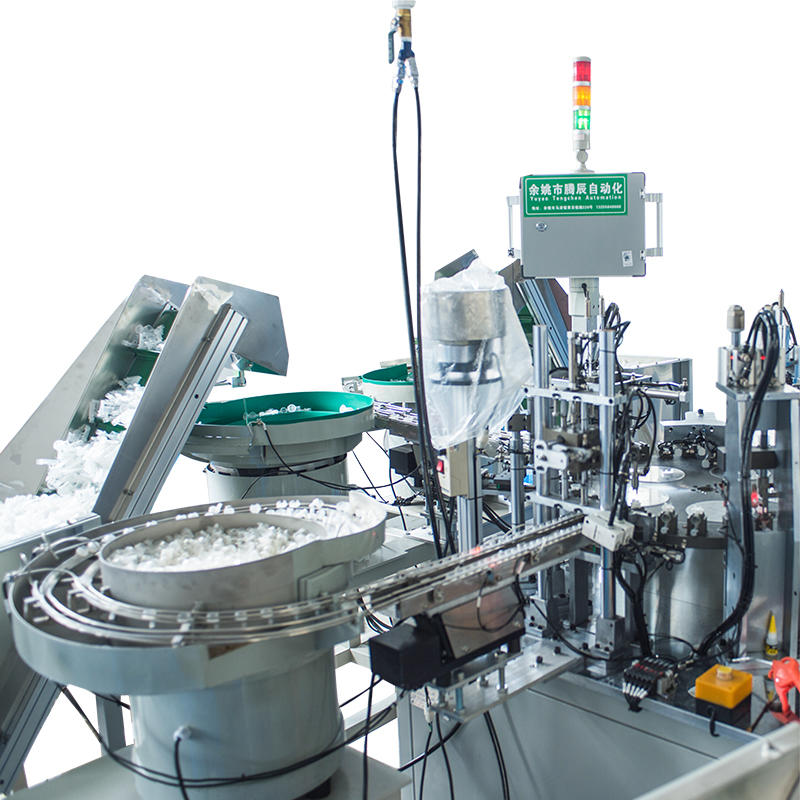
Vibratory or Centrifugal Feeders with Orientation Control: Feeding systems such as vibratory bowls or centrifugal feeders are fundamental to achieving reliable alignment before assembly begins. These systems are engineered to sort, orient, and feed each component—whether asymmetrical caps or flexible rubber bulbs—into the machine in a uniform position. This is achieved using specialized internal tracks, air nozzles, sensors, and reject gates that monitor orientation continuously. For instance, if a rubber bulb is upside down or a glass tube is angled, optical sensors detect the fault and route the part back into the orientation cycle or remove it entirely, ensuring that all parts entering the assembly area are ready for accurate alignment and handling.
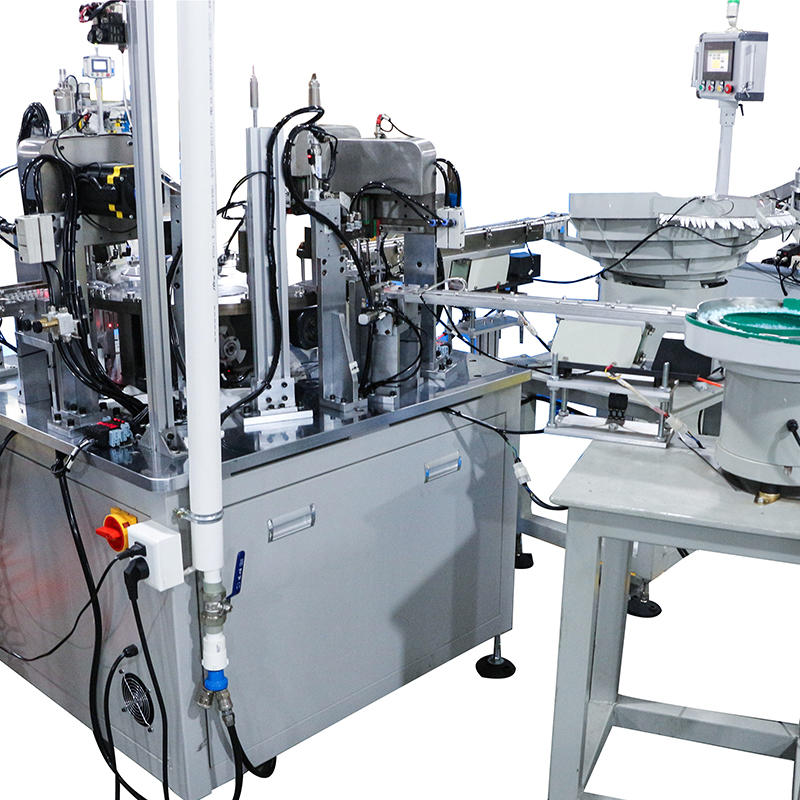
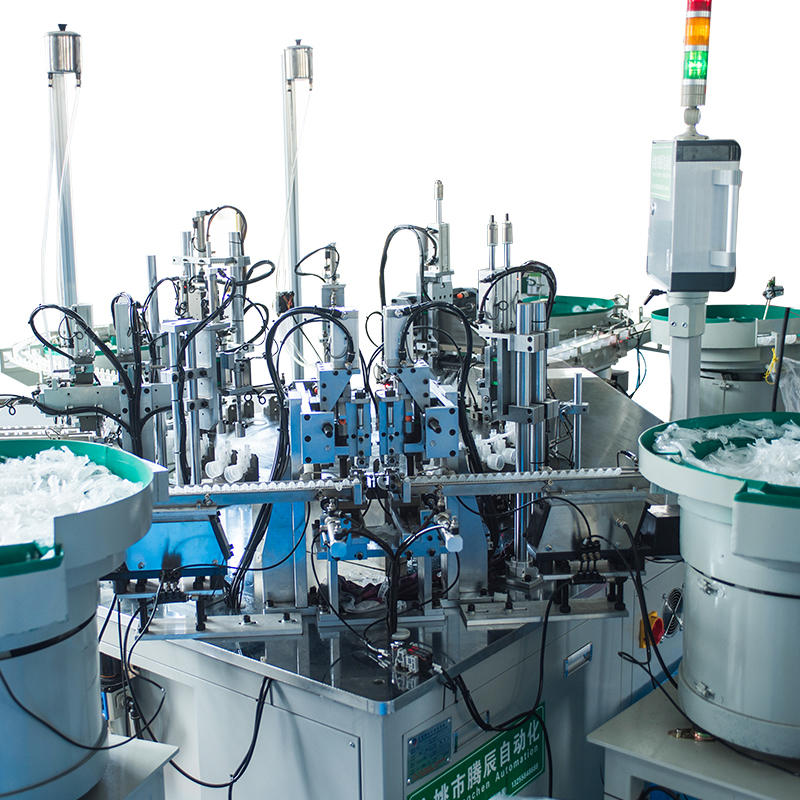
Precision Pick-and-Place Systems with Vacuum or Servo Control: Once components are properly oriented and staged, pick-and-place systems retrieve and insert them into the assembly mechanism with micron-level precision. These systems often include multi-axis robotic arms or linear gantries controlled by servo motors for consistent speed and positional accuracy. For delicate components like thin-walled glass tubes, vacuum grippers are employed to prevent scratches or breakage. The integration of servo technology allows for speed ramping and soft-landing motion, which ensures the exact placement angle and depth are achieved every time. These systems are finely tuned to maintain alignment across thousands of repetitions, which is especially critical in sterile or cosmetic applications where presentation and performance must both be flawless.
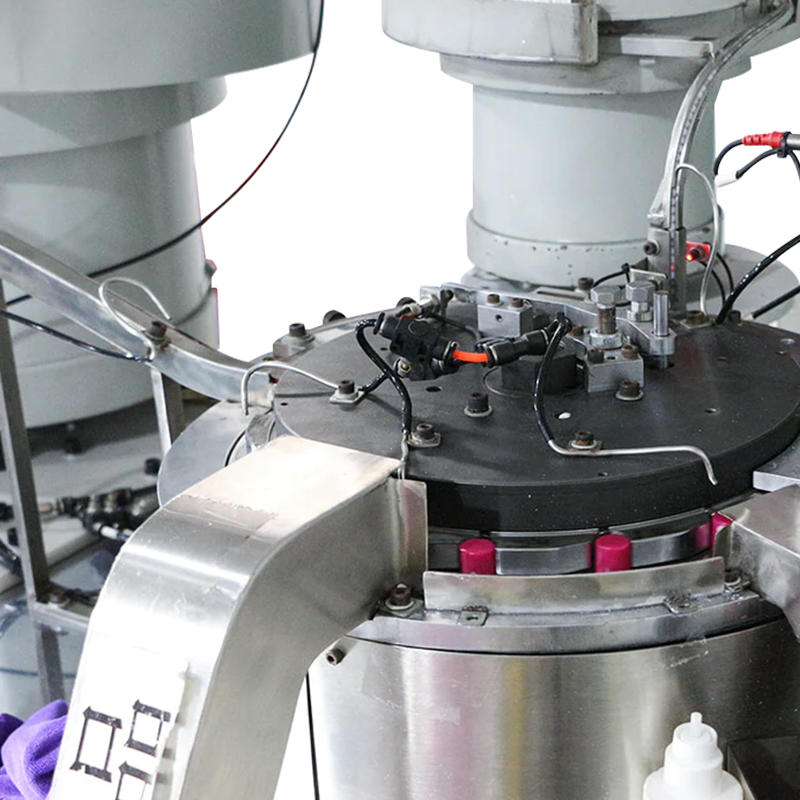
Integrated Vision Systems and Laser Sensors for Position Verification: High-end dropper assembly machines are often equipped with inline vision inspection systems that utilize industrial-grade cameras with AI-driven image processing algorithms. These systems analyze each part’s position and rotational alignment in real time—before and after each assembly step. Coupled with laser triangulation sensors or diffuse reflective photoelectric sensors, the system can detect a misalignment as small as 0.1 mm. If deviation is detected, the system flags the assembly and diverts it to a reject channel, ensuring continuous output quality without halting production. The vision system can also monitor wear trends and inform predictive maintenance schedules.
Mechanical Guides and Nesting Fixtures for Repeatable Placement: The assembly platform includes high-precision mechanical nests or cavities, typically made of machined aluminum or stainless steel, that cradle each part during assembly. These fixtures are custom-designed to match the dimensions of each component with extremely tight tolerances—ensuring no movement occurs during placement, even under high actuation speed or vibration. Nests may include compression pads, pneumatic clamps, or spring-loaded holders that secure parts during pick-up and release stages.





 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى