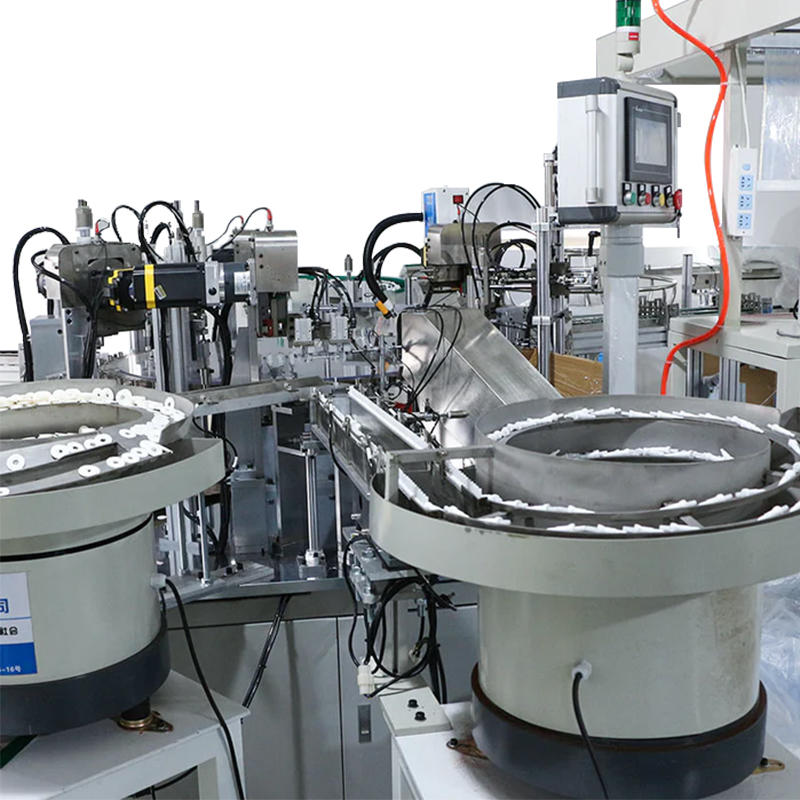
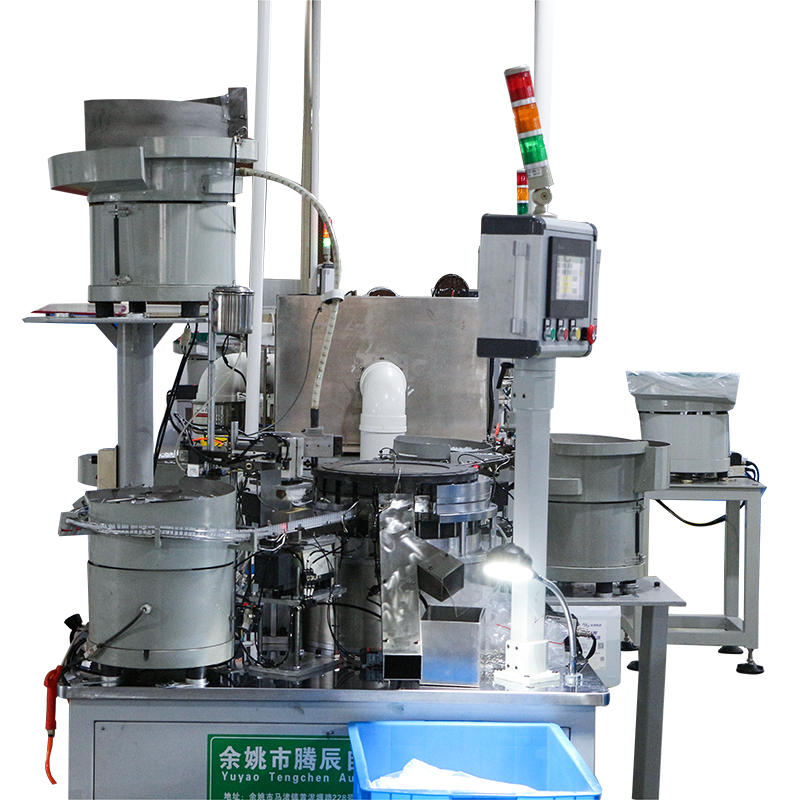
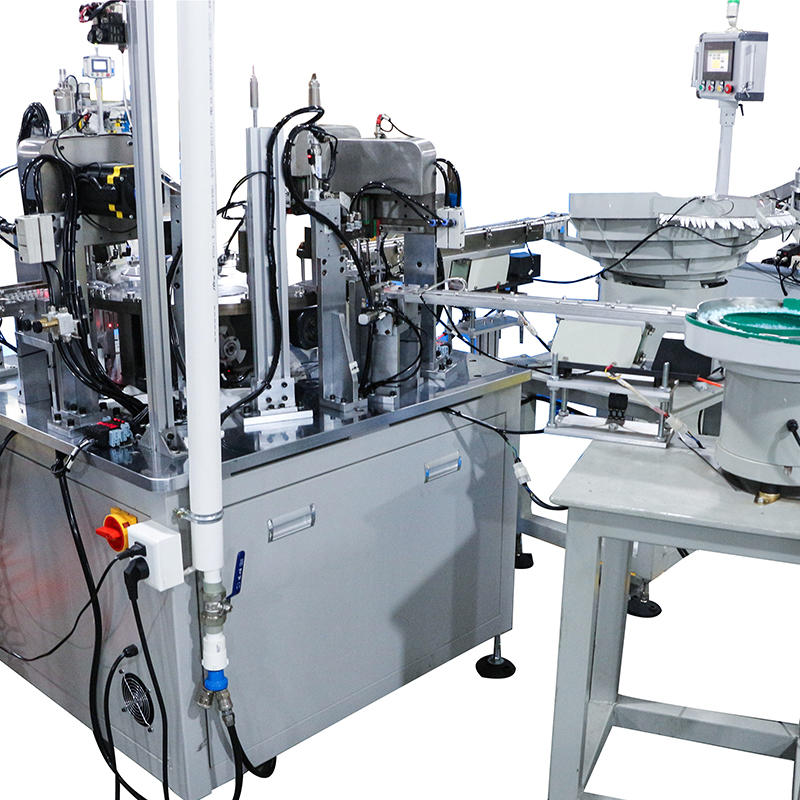
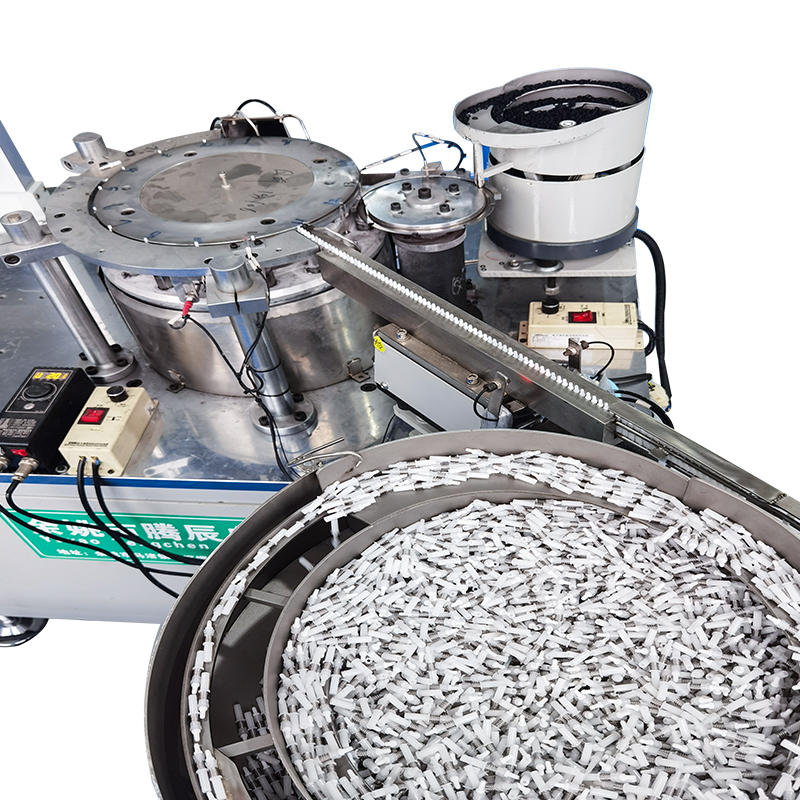
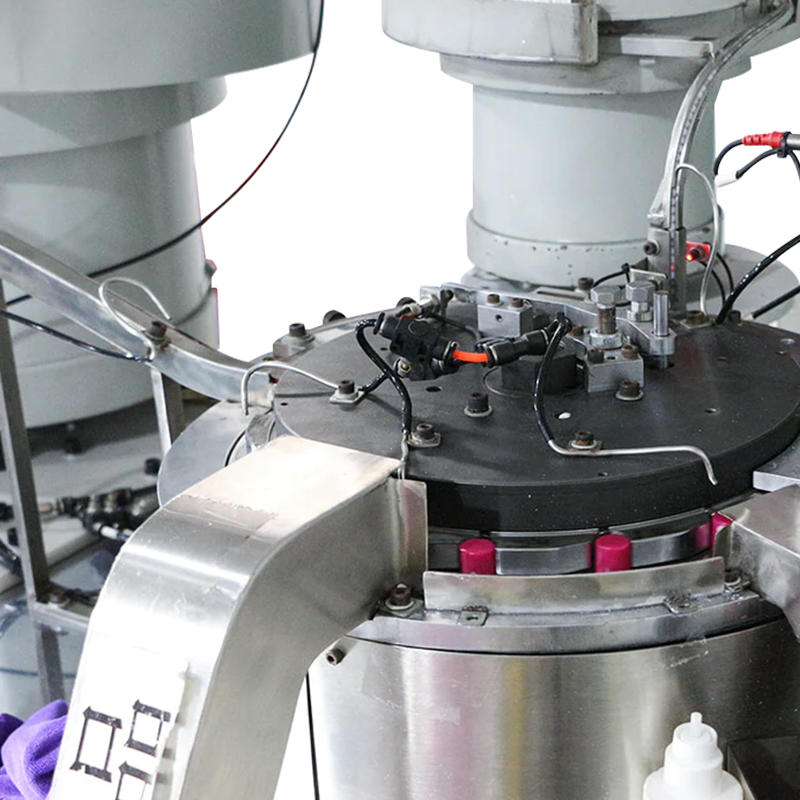
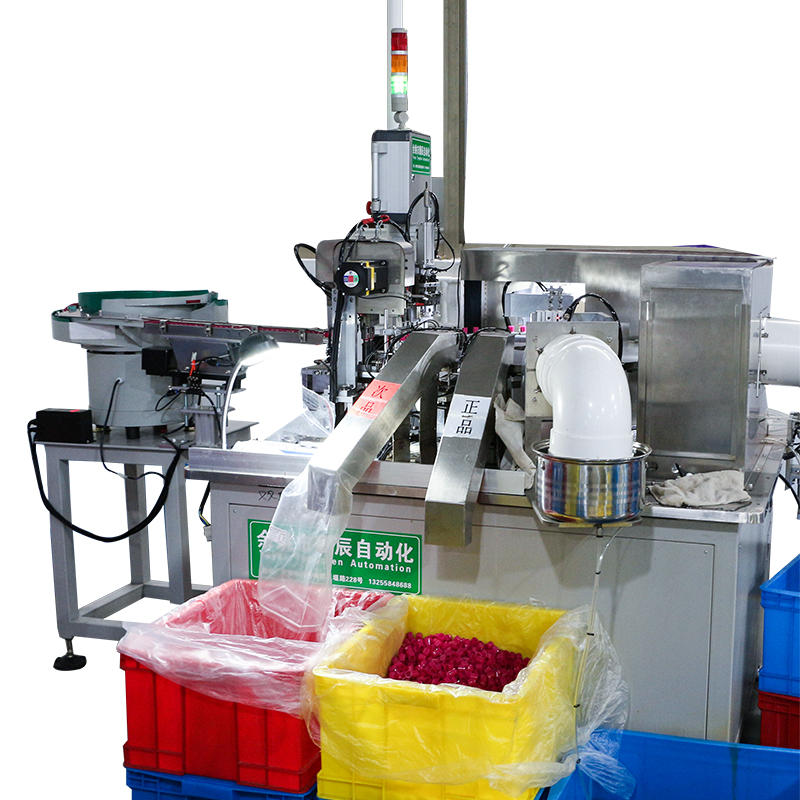
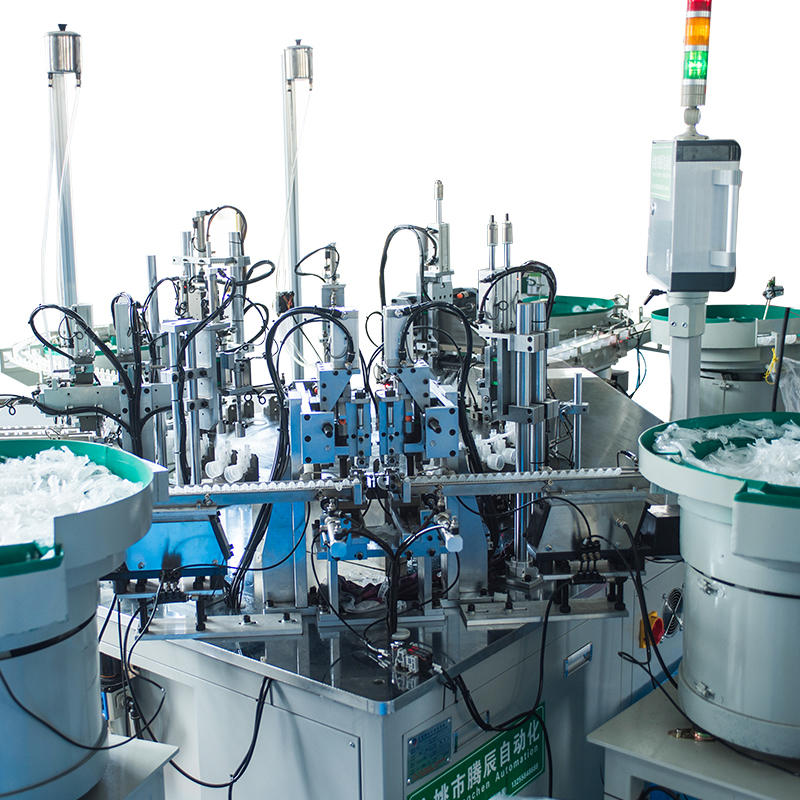
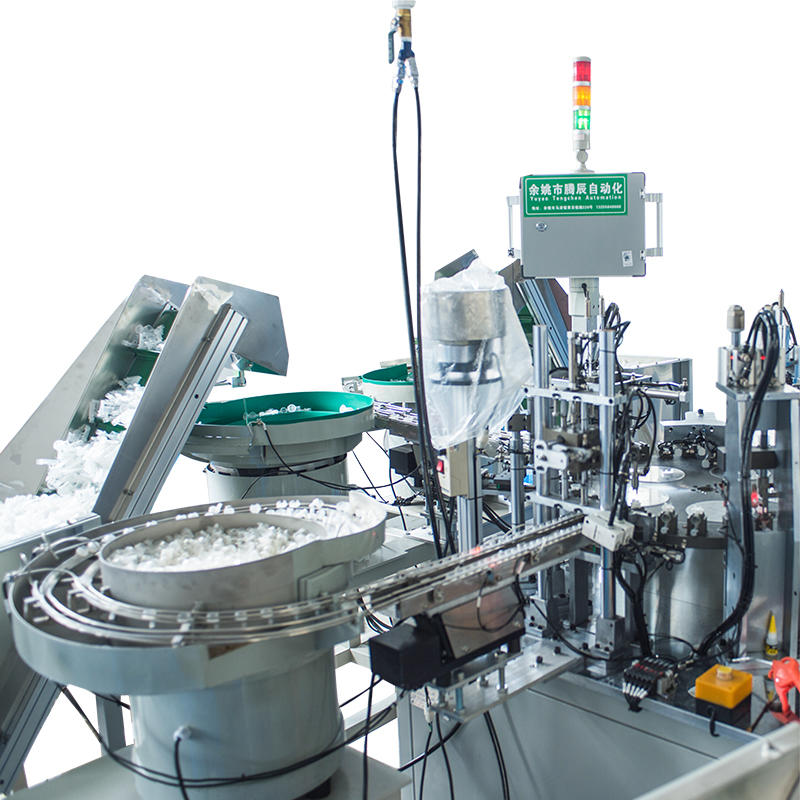
The Pneumatic Vacuum Testing Machine relies on precise sensors to continuously monitor the pressure levels within the testing chamber during the test cycle. When assessing for leaks, the machine establishes a baseline vacuum pressure and continuously tracks any changes. In the event of a vacuum drop, the system evaluates the rate of pressure change. External factors, such as variations in ambient temperature, can affect the internal pressure of the chamber, causing minor fluctuations. The machine’s software algorithms are designed to differentiate between these harmless, temporary shifts and significant, sustained drops in pressure that are indicative of leaks caused by material defects. For example, temperature-induced pressure changes typically happen gradually and can be correlated with known temperature fluctuations, while leaks due to defects tend to result in a more consistent or rapid pressure drop.
To ensure that external environmental factors do not interfere with the accuracy of testing, some advanced Pneumatic Vacuum Testing Machines are equipped with built-in environmental compensation systems. These systems continuously measure ambient temperature, humidity, and barometric pressure to detect any potential environmental influences that could affect the results. By incorporating these real-time environmental measurements into the test cycle, the machine adjusts its pressure readings accordingly, ensuring that temperature-induced fluctuations are accounted for. This allows the testing process to remain focused on detecting genuine leaks caused by defects in the tested materials rather than erroneously attributing small variations to external factors like temperature or humidity changes.
The sensitivity of the Pneumatic Vacuum Testing Machine is a key factor in identifying whether a pressure drop is due to a material defect or external influences. Modern machines feature advanced leak detection systems that can accurately measure even the smallest changes in pressure, down to minute fractions of a vacuum. When a small leak is detected, the machine will compare the rate and magnitude of the pressure drop against predetermined thresholds and patterns. If the leak rate is consistent with environmental changes such as temperature fluctuations, the system may dismiss the reading as a result of those influences. However, if the pressure drop occurs consistently over a prolonged period and does not correlate with environmental conditions, the machine will flag it as a potential material defect.
To mitigate the impact of environmental variables on the test results, the Pneumatic Vacuum Testing Machine typically undergoes a pre-test calibration phase. During this phase, the machine measures the baseline pressure under the specific environmental conditions of the testing area, ensuring that any temperature, humidity, or atmospheric pressure deviations are incorporated into the initial reading. The calibration process compensates for common fluctuations caused by the environment, allowing the machine to adjust the test results accordingly. Once calibrated, the machine can differentiate between normal environmental pressures and abnormal vacuum loss caused by defects in the material being tested, increasing the accuracy of the results.
Some advanced Pneumatic Vacuum Testing Machines feature dynamic adjustment capabilities that continuously adapt to short-term environmental changes, such as sudden temperature fluctuations or rapid shifts in humidity. These adjustments are particularly beneficial when testing in environments where external conditions can change unpredictably, such as in manufacturing facilities with varying ambient temperatures or outdoor testing areas. The machine’s sensors constantly monitor the surrounding environment, and if they detect a sudden environmental shift, the system can adjust the test parameters in real time. This feature helps to isolate genuine leaks caused by material defects from those that are merely a result of temporary external influences, ensuring that the vacuum test remains accurate and consistent.





 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى