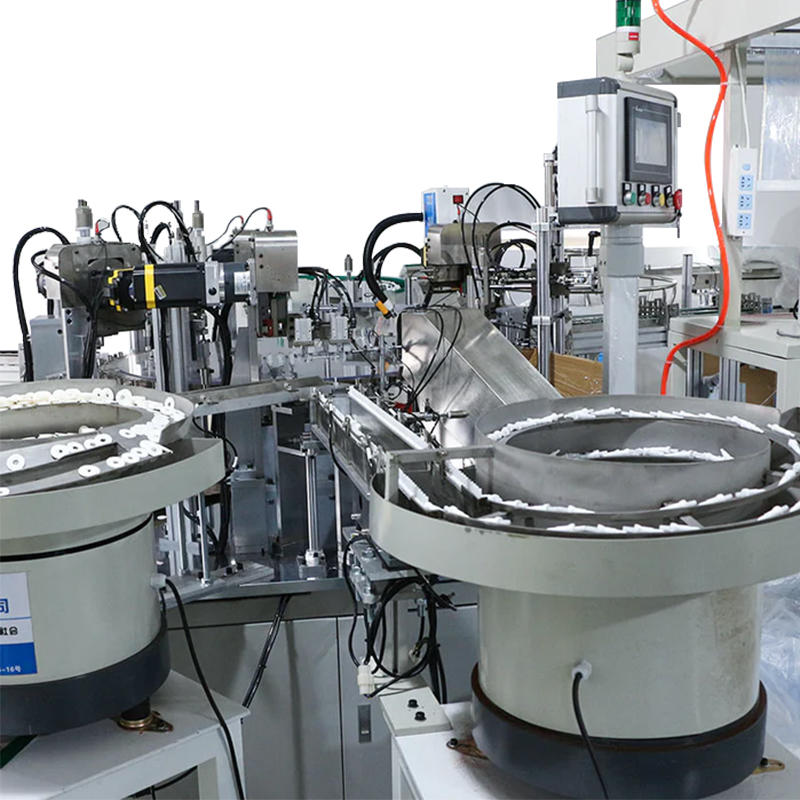
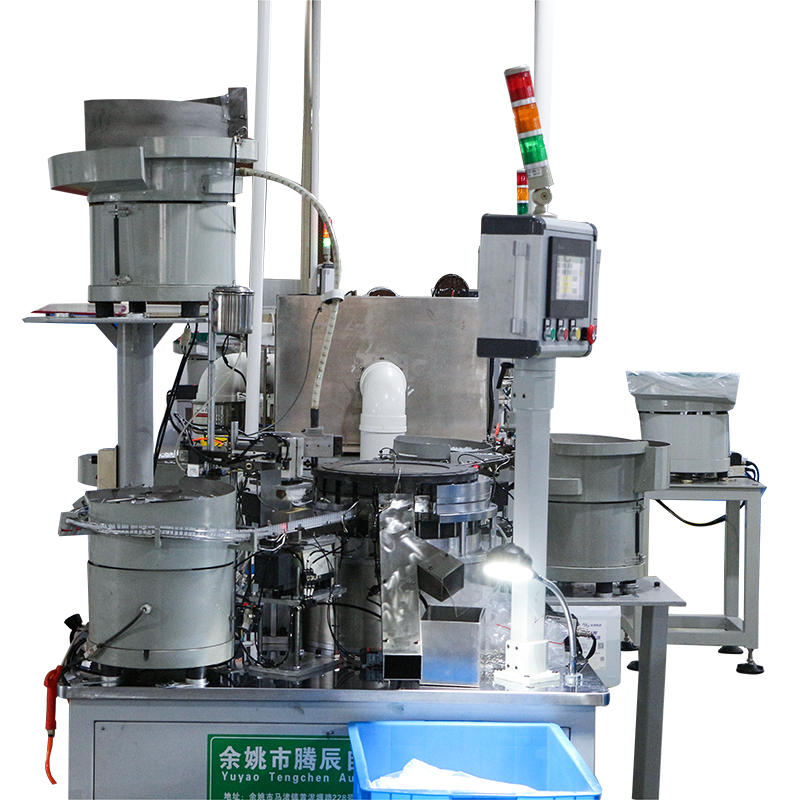
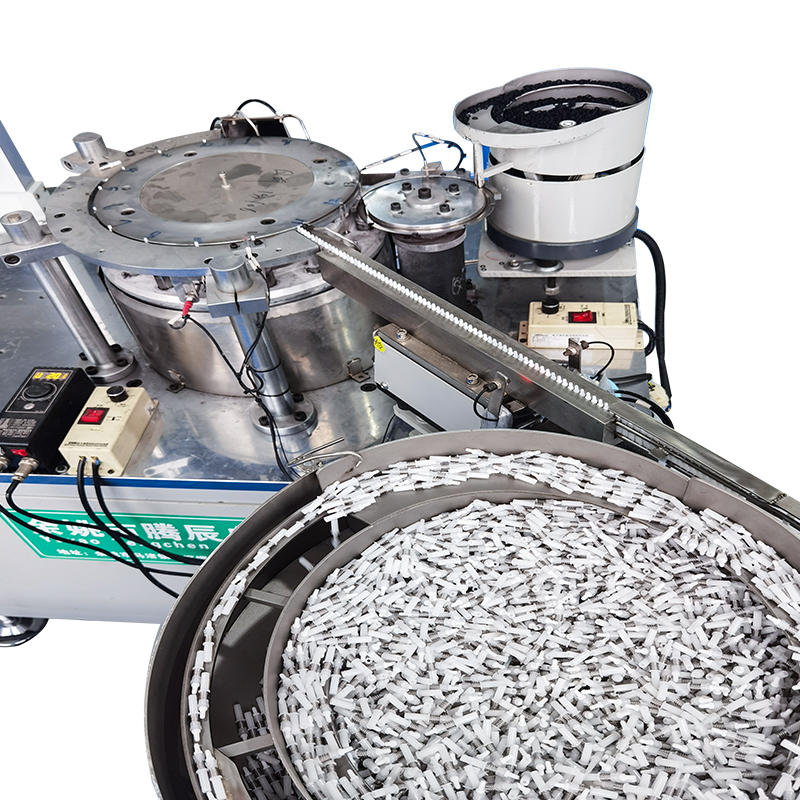
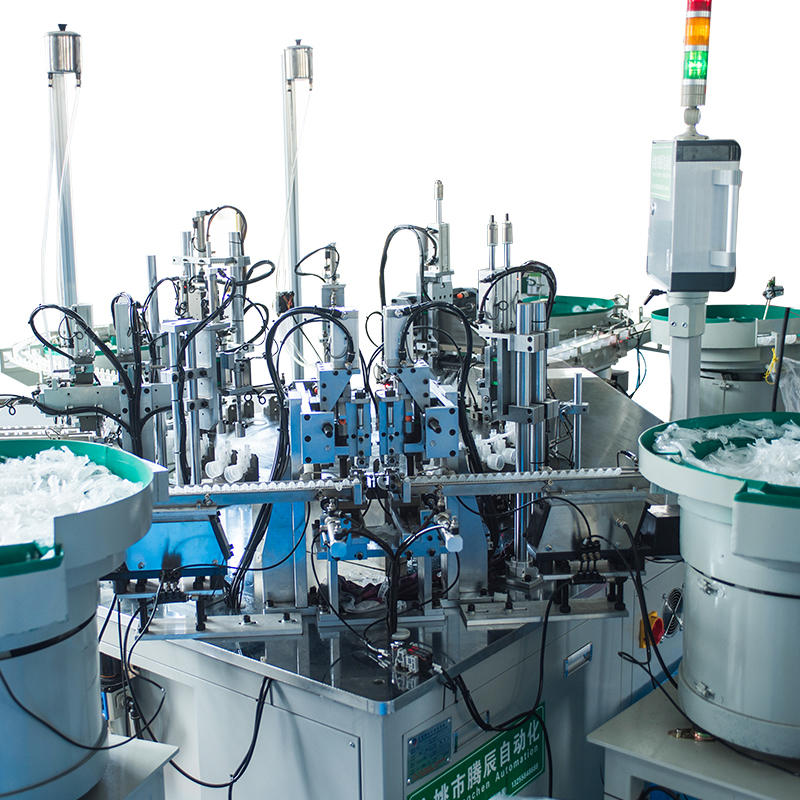
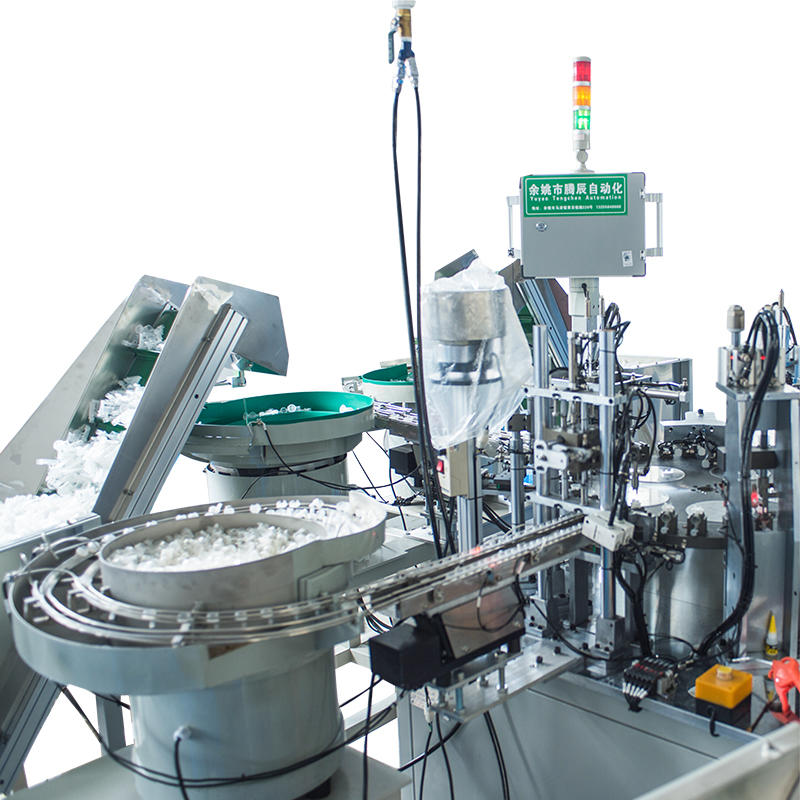
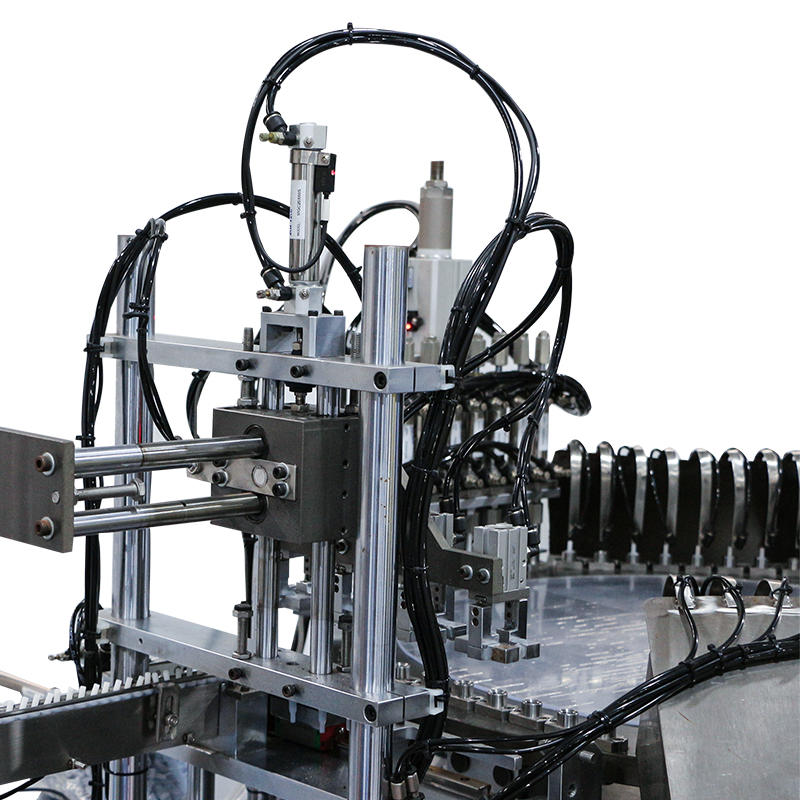
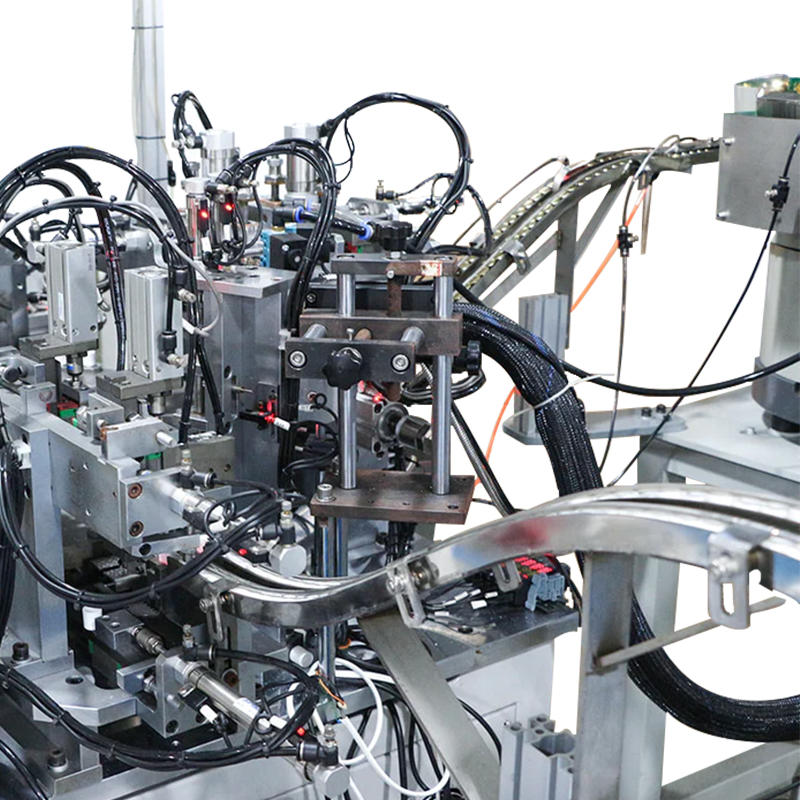
The razor blade assembly machine incorporates automated feeders or magazines designed to reliably supply components, such as lubricating strips and handles, to the assembly line. These automated feeders can be configured to feed components in precise quantities and at consistent intervals, ensuring that the right amount of material is delivered at the right time to match the machine's throughput. The feeders are capable of handling various component sizes and shapes, allowing the machine to maintain production efficiency while reducing human intervention. Depending on the machine's design, the system may use vibratory bowls, linear conveyors, or pick-and-place systems to move components into position without the risk of damaging sensitive parts.
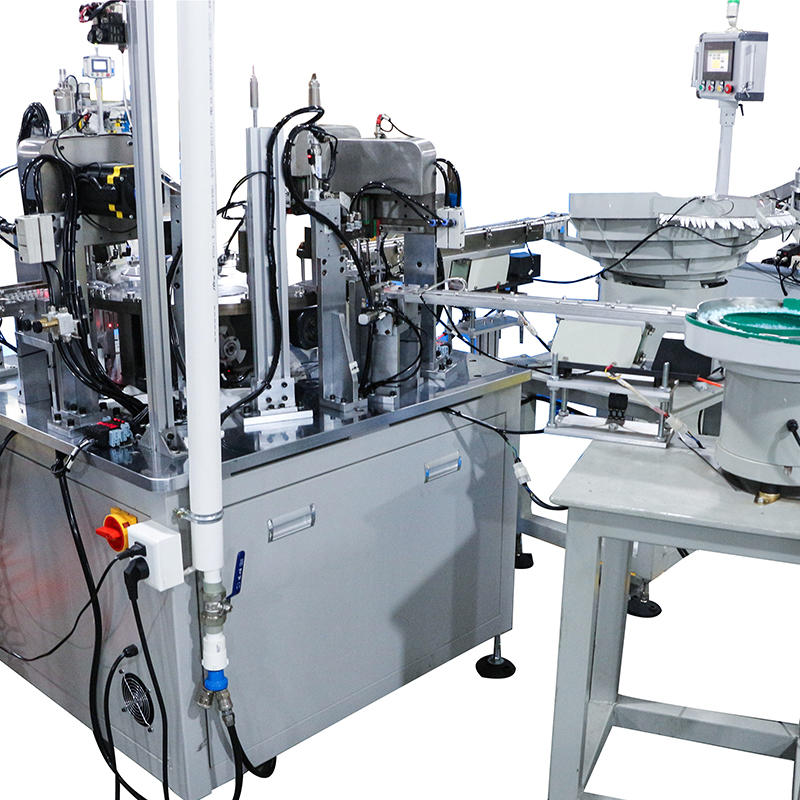
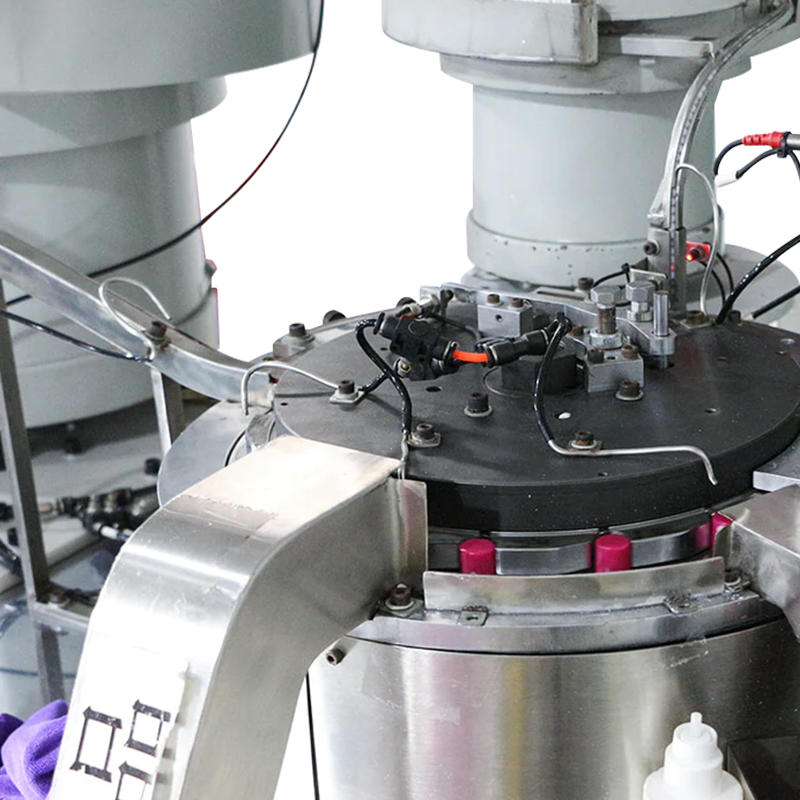
The process of placing components like lubricating strips or handles onto the razor blade is achieved with high precision, facilitated by pick-and-place mechanisms. These mechanisms use either robotic arms, vacuum suction cups, or mechanical grippers to securely pick up and position components onto the blade. The vacuum suction system is particularly effective for placing smaller or thinner components, such as lubricating strips, with minimal risk of shifting or misalignment. The gripper systems used for handles ensure they are positioned securely on the blade while also preventing damage to the components. The precision in placement is crucial for ensuring that components are attached securely and uniformly, which ultimately affects the overall performance and quality of the final product.
Accurate orientation and alignment are crucial to ensure proper fit and function, especially for components like lubricating strips, which need to be symmetrically placed for optimal performance. The razor blade assembly machine often includes a system of orientation guides or alignment sensors that ensure each component is correctly positioned before being attached. For example, rotary indexing mechanisms may be used to ensure that handles are placed with the correct orientation, while sensor-controlled guides ensure that lubricating strips are applied with the correct surface facing the blade. These systems are designed to minimize the risk of misplacement, thereby improving both the efficiency of the assembly process and the quality of the final product.
Once the components are placed in their designated positions, the razor blade assembly machine employs various compression or bonding mechanisms to securely attach them. For example, heat-pressing or adhesive bonding is used to firmly attach lubricating strips to the blade, ensuring that they stay in place during use without peeling or shifting. For handles, the assembly machine may use snap-fit systems, ultrasonic welding, or mechanical fastening techniques to secure the handle in place without damaging the blade or handle material. These bonding mechanisms are designed to ensure a long-lasting and strong attachment, contributing to the overall durability and functionality of the razor blade.
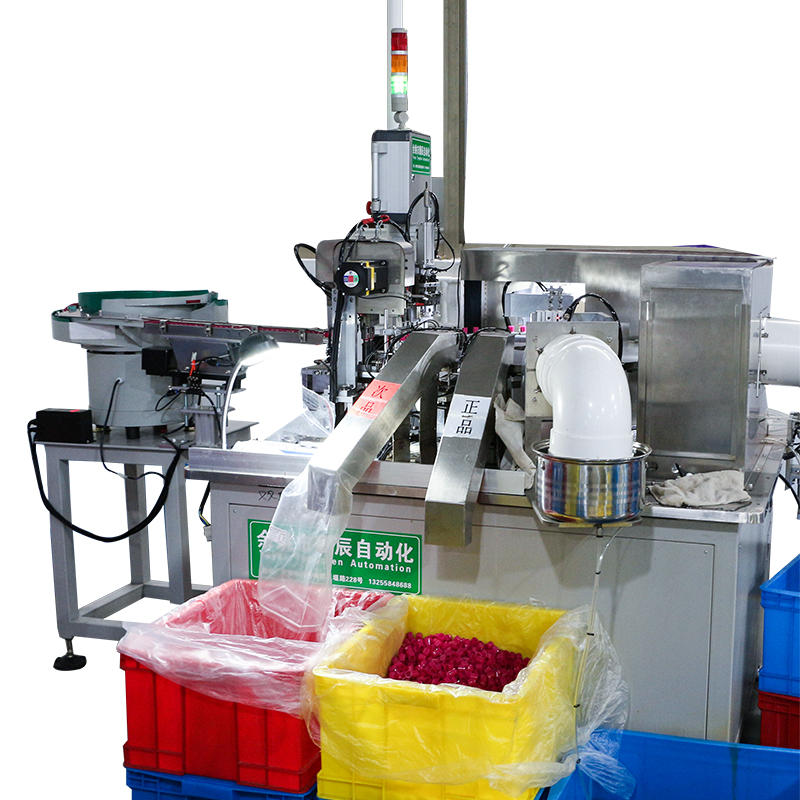
Throughout the entire assembly process, the razor blade assembly machine integrates various quality control systems to ensure that each component is correctly inserted and that the assembly meets the required standards. Vision systems, laser scanners, and force sensors are often used to detect any misalignment, component defects, or improper assembly. For instance, vision systems may use cameras and image processing software to verify that the lubricating strips are placed symmetrically and that handles are attached securely to the razor blade. If any errors or defects are detected, the machine can trigger an alert, and a reject mechanism can automatically discard or separate the defective product from the assembly line.





 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى